In Situ and Operando NMR Techniques
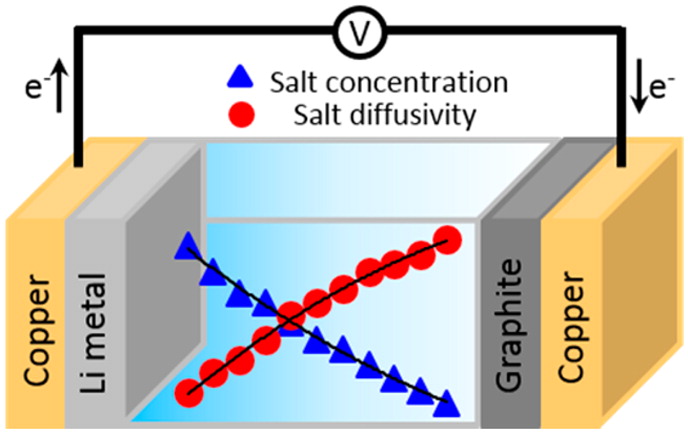
In order to successfully model the transient conditions within a battery during operation, reliable data on the transport properties of electrolyte solutions are absolutely imperative. The accurate characterization of these ion transport parameters is a complex problem, as the values of ionic diffusion coefficients in an electrolyte solution depend strongly on the salt concentration, which is neither stationary nor homogeneous during operation. In the Goward group, we use an in situ magnetic resonance imaging technique for in operando visualization of the ion distribution in Li-ion battery electrolytes during battery operation with simultaneous extraction of the elusive ion transport parameters. We have been able to show that the diffusion coefficient (D) has a significant dependence on the salt concentration, with the values of D measured at opposite ends of the cell varying by more than 60%. Such changes obviously must be taken into account in order to provide an accurate description of mass-transport. Moreover, the concentration gradient generated within the cell affects not only the mass transport in electrolyte solution, but also the overall electrode lithiation. Ultimately, in situ determination of the Li concentration profile and other transport phenomena in electrodes from 7Li magnetic resonance images collected during the cycling of a cell allows us to contribute to a more accurate electrochemical model that can be used in battery management systems for automotive applications.